电视输入框架 (TIF) 管理器与音频路由 API 协同工作,以支持灵活的音频路径更改。当片上系统 (SoC) 实现电视硬件抽象层 (HAL) 时,每个电视输入(HDMI IN、Tuner 等)都会提供 TvInputHardwareInfo,其中指定了音频类型和地址的 AudioPort 信息。
- 物理音频输入/输出设备具有相应的 AudioPort。
- 软件音频输出/输入流表示为 AudioMixPort(AudioPort 的子类)。
然后,TIF 使用 AudioPort 信息进行音频路由 API。
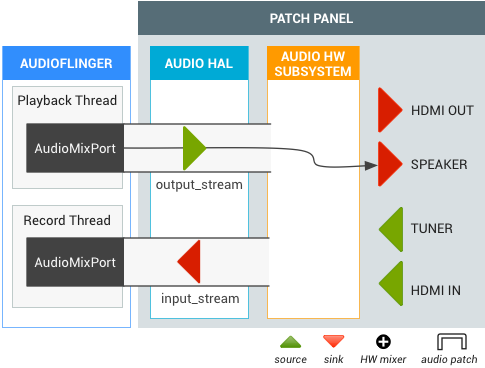
图 1. 电视输入框架 (TIF)
要求
SoC 必须实现音频 HAL,并支持以下音频路由 API
| 音频端口 |
|
|---|---|
| 默认输入 | AudioRecord(使用 DEFAULT 输入源创建)必须在 Android TV 上针对 AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_DEFAULT 采集获取虚拟空输入源。 |
| 设备环回 | 需要支持 AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK 输入,该输入是所有电视输出的完整音频输出混音(11Khz、16 位单声道或 48Khz、16 位单声道)。仅用于音频捕获。 |
电视音频设备
Android 支持以下音频设备用于电视音频输入/输出。
system/media/audio/include/system/audio.h
注意: 在 Android 5.1 及更早版本中,此文件的路径为: system/core/include/system/audio.h
/* output devices */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL = 0x400, AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI = AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL, /* HDMI Audio Return Channel */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC = 0x40000, /* S/PDIF out */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF = 0x80000, /* input devices */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_AUX_DIGITAL = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x20, AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_HDMI = AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_AUX_DIGITAL, /* TV tuner input */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_TV_TUNER = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x4000, /* S/PDIF in */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_SPDIF = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x10000, AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x40000,
音频 HAL 扩展
音频路由 API 的音频 HAL 扩展由以下内容定义
system/media/audio/include/system/audio.h
注意: 在 Android 5.1 及更早版本中,此文件的路径为: system/core/include/system/audio.h
/* audio port configuration structure used to specify a particular configuration of an audio port */
struct audio_port_config {
audio_port_handle_t id; /* port unique ID */
audio_port_role_t role; /* sink or source */
audio_port_type_t type; /* device, mix ... */
unsigned int config_mask; /* e.g. AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_ALL */
unsigned int sample_rate; /* sampling rate in Hz */
audio_channel_mask_t channel_mask; /* channel mask if applicable */
audio_format_t format; /* format if applicable */
struct audio_gain_config gain; /* gain to apply if applicable */
union {
struct audio_port_config_device_ext device; /* device specific info */
struct audio_port_config_mix_ext mix; /* mix specific info */
struct audio_port_config_session_ext session; /* session specific info */
} ext;
};
struct audio_port {
audio_port_handle_t id; /* port unique ID */
audio_port_role_t role; /* sink or source */
audio_port_type_t type; /* device, mix ... */
unsigned int num_sample_rates; /* number of sampling rates in following array */
unsigned int sample_rates[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_SAMPLING_RATES];
unsigned int num_channel_masks; /* number of channel masks in following array */
audio_channel_mask_t channel_masks[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_CHANNEL_MASKS];
unsigned int num_formats; /* number of formats in following array */
audio_format_t formats[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_FORMATS];
unsigned int num_gains; /* number of gains in following array */
struct audio_gain gains[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_GAINS];
struct audio_port_config active_config; /* current audio port configuration */
union {
struct audio_port_device_ext device;
struct audio_port_mix_ext mix;
struct audio_port_session_ext session;
} ext;
};
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
struct audio_hw_device {
:
/**
* Routing control
*/
/* Creates an audio patch between several source and sink ports.
* The handle is allocated by the HAL and should be unique for this
* audio HAL module. */
int (*create_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
unsigned int num_sources,
const struct audio_port_config *sources,
unsigned int num_sinks,
const struct audio_port_config *sinks,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle);
/* Release an audio patch */
int (*release_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_patch_handle_t handle);
/* Fills the list of supported attributes for a given audio port.
* As input, "port" contains the information (type, role, address etc...)
* needed by the HAL to identify the port.
* As output, "port" contains possible attributes (sampling rates, formats,
* channel masks, gain controllers...) for this port.
*/
int (*get_audio_port)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
struct audio_port *port);
/* Set audio port configuration */
int (*set_audio_port_config)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
const struct audio_port_config *config);
测试 DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK
要测试用于电视监控的 DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK,请使用以下测试代码。运行测试后,捕获的音频将保存到 /sdcard/record_loopback.raw,您可以使用 FFmpeg 听取它。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
AudioRecord mRecorder;
Handler mHandler = new Handler();
int mMinBufferSize = AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize(RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE,
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT);;
static final int RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE = 48000;
public void doCapture() {
mRecorder = new AudioRecord(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.DEFAULT, RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE,
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO, AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT, mMinBufferSize * 10);
AudioManager am = (AudioManager) getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
ArrayList<AudioPort> audioPorts = new ArrayList<AudioPort>();
am.listAudioPorts(audioPorts);
AudioPortConfig srcPortConfig = null;
AudioPortConfig sinkPortConfig = null;
for (AudioPort audioPort : audioPorts) {
if (srcPortConfig == null
&& audioPort.role() == AudioPort.ROLE_SOURCE
&& audioPort instanceof AudioDevicePort) {
AudioDevicePort audioDevicePort = (AudioDevicePort) audioPort;
if (audioDevicePort.type() == AudioManager.DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK) {
srcPortConfig = audioPort.buildConfig(48000, AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_DEFAULT,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_DEFAULT, null);
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Found loopback audio source port : " + audioPort);
}
}
else if (sinkPortConfig == null
&& audioPort.role() == AudioPort.ROLE_SINK
&& audioPort instanceof AudioMixPort) {
sinkPortConfig = audioPort.buildConfig(48000, AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_DEFAULT,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_DEFAULT, null);
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Found recorder audio mix port : " + audioPort);
}
}
if (srcPortConfig != null && sinkPortConfig != null) {
AudioPatch[] patches = new AudioPatch[] { null };
int status = am.createAudioPatch(
patches,
new AudioPortConfig[] { srcPortConfig },
new AudioPortConfig[] { sinkPortConfig });
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Result of createAudioPatch(): " + status);
}
mRecorder.startRecording();
processAudioData();
mRecorder.stop();
mRecorder.release();
}
private void processAudioData() {
OutputStream rawFileStream = null;
byte data[] = new byte[mMinBufferSize];
try {
rawFileStream = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(new File("/sdcard/record_loopback.raw")));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Can't open file.", e);
}
long startTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeMs < 5000) {
int nbytes = mRecorder.read(data, 0, mMinBufferSize);
if (nbytes <= 0) {
continue;
}
try {
rawFileStream.write(data);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Error on writing raw file.", e);
}
}
try {
rawFileStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Exit audio recording.");
}
在 /sdcard/record_loopback.raw 中找到捕获的音频文件,并使用 FFmpeg 听取它
adb pull /sdcard/record_loopback.rawffmpeg -f s16le -ar 48k -ac 1 -i record_loopback.raw record_loopback.wavffplay record_loopback.wav
用例
本节包括电视音频的常见用例。
带扬声器输出的电视调谐器
当电视调谐器变为活动状态时,音频路由 API 会在调谐器和默认输出(例如扬声器)之间创建音频通路。调谐器输出不需要解码,但最终音频输出与软件 output_stream 混合。
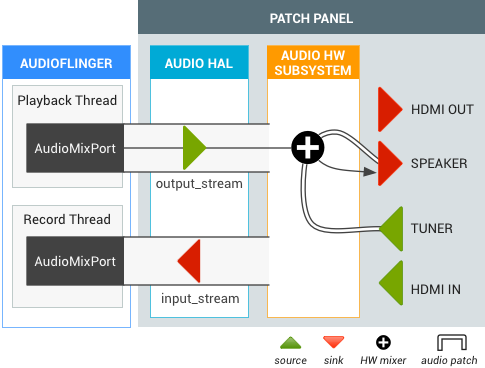
图 2. 带扬声器输出的电视调谐器的音频通路。
直播电视期间的 HDMI 输出
用户正在观看直播电视,然后切换到 HDMI 音频输出 (Intent.ACTION_HDMI_AUDIO_PLUG)。所有 output_stream 的输出设备都更改为 HDMI_OUT 端口,并且 TIF 管理器将现有调谐器音频通路的接收端口更改为 HDMI_OUT 端口。

图 3. 来自直播电视的 HDMI 输出的音频通路。
